Understanding Common Skin Issues: Causes and Scientific Perspectives
Our skin is the largest organ in the body and serves as a protective barrier against external threats. However, it is also susceptible to various skin issues affecting its appearance and health.
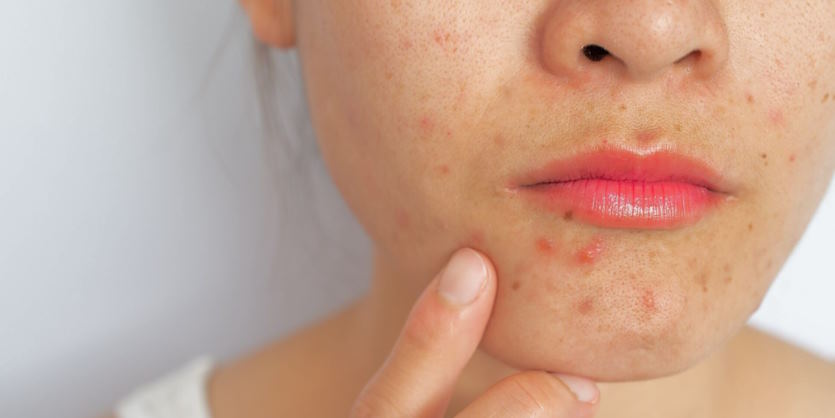
Acne
Acne is a prevalent skin condition that affects people of all ages, particularly during adolescence. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, forming whiteheads, blackheads, pimples, and sometimes deeper cysts.
Scientific Perspective
Acne is primarily caused by the overproduction of sebum, an oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands in the skin. Hormonal changes, especially during puberty, can stimulate the sebaceous glands, increasing sebum production. Additionally, the buildup of dead skin cells and bacteria (such as Propionibacterium acnes) in the clogged follicles contributes to the inflammatory response that results in red and swollen acne lesions.

Wrinkles
Wrinkles are a natural part of the aging process and are characterized by fine lines and creases that develop on the skin’s surface, particularly in areas exposed to the sun, like the face and neck.
Scientific Perspective
Collagen and elastin are essential proteins that provide structure and elasticity to the skin. As we age, collagen and elastin production decreases, leading to a loss of skin elasticity and firmness. Additionally, repetitive facial expressions and external factors such as UV radiation from the sun and environmental pollutants can break down collagen and elastin fibers, contributing to the formation of wrinkles.
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation refers to the darkening of certain areas of the skin, resulting in patches or spots that are darker than the surrounding skin tone. Common types of hyperpigmentation include sunspots, melasma, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Scientific Perspective
The primary cause of hyperpigmentation is an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. When the skin is exposed to UV radiation from the sun, it triggers the melanocytes (melanin-producing cells) to produce more melanin to protect the skin from damage. However, this can lead to uneven distribution of melanin, causing dark spots on the skin.